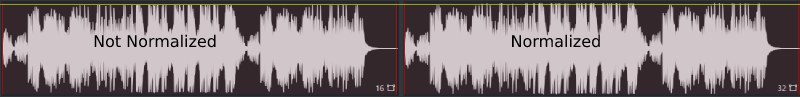
Normalization does not affect the quality of the audio. Normalization adjusts the entire audio signal by a fixed amount bringing it to the target level, typically between -1dB and 0dB.
What Does Normalization Do?
Normalization adjusts the audio based on the highest signal level or perceived loudness to bring the audio signal to a target level. It does this by applying a fixed amount of gain to the audio signal to bring it to the target level, typically -1dB or 0dB.
During the normalization process, the DAWs algorithm identifies the highest audio peaks in the digital sample bits. It then calculates the difference between the highest value and the target value (in dB). The result is then applied to each audio sample bit to bring the audio signal to the target value.
Normalizing the signal-to-noise ratio and relative dynamics will leave the audio signal unchanged because the same amount of gain is applied across the entire audio recording.
Types Of Normalization
There are two types of normaization algorithms.
- Peak Normalization
- Loudness Normalization
What Is Peak Normalization?
Peak normalization increases the audio signal by a fixed value based on the difference between the peak audio signal and the normalization target value.
Peak normalization takes the audio’s highest signal peak, calculates the difference between it and the target value (like -1dB), and then evenly increases the entire audio signal by the difference.
What Is Loudness Normalization?
Loudness normalization adjusts the audio based on the perceived loudness of the track. The perceived loudness is determined by the Loudness Units relative to Full Scale (LUFS) measurement that factors human perception and the audio signal together.
Loudness normalization was introduced to help stop the varying loudness between different songs. Ever listen to a newer song followed by an original recording of The Beatles? The song by The Beatles will sound so quiet compared to the newer song.
Using Loudness Normalization and the LUFS measurement both the modern song and the older Beatles song will sound much closer in volume. The standard of audio normalization level is used in music streaming to movies.
This means less volume knob turning and having not being blasted by a wall of sound after you’re done listening to a quiet song.
Can Normalization Introduce Clipping?
Peak Normalization will not introduce clipping as it normalizes the peak audio level to 0dB or under, while Loudness Normalization can introduce clipping if the dynamic range of the audio and the target normalization level results in a value exceeding 0dB or the software limits.
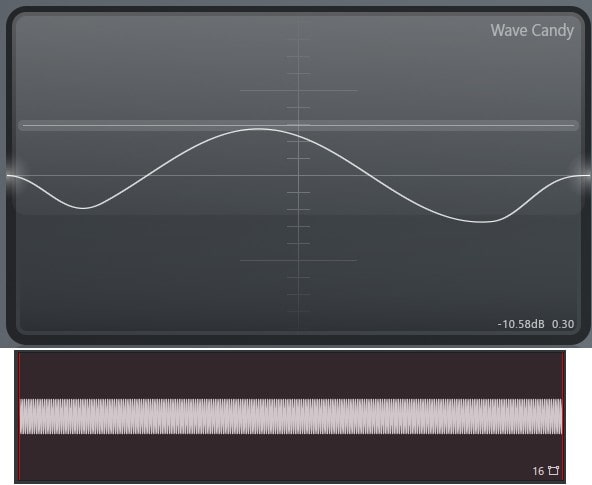
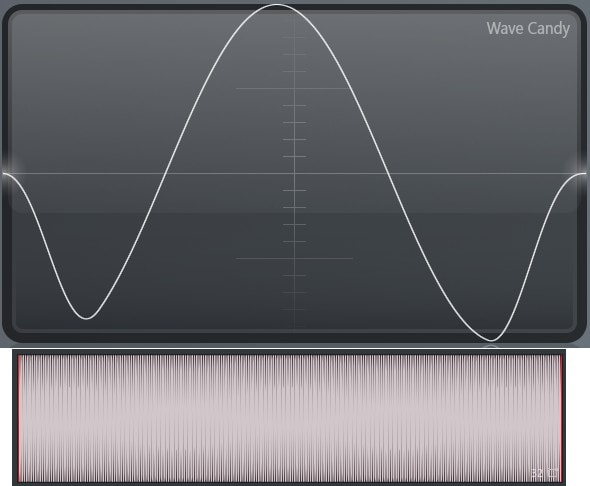
Most software with normalization provides the option of using dynamic range compression to prevent clipping. Using compression will alter the audios signal-to-noise ratio and relative dynamics.
Summary
Audio Normalization does not alter the sound quality of the given audio; however, when using loudness normalization there is a chance that the signal may clip if the dynamic range of the audio and the target normalization level results in a value exceeding 0dB.
